Processes & Process Areas
Processes & Process Areas
Overview
Processes are specific recipes or procedures with defined parameters that can be performed on resources. Each process contains step-by-step instructions and exact settings (time, temperature, power, flow rates, etc.) needed to complete an operation.
Process Areas are simple taxonomies that group resources by category (e.g., Electronics, Textiles, Woodworking, Packaging, Wet Processing).
Key Concepts:
- Processes are recipes with specific parameters and steps
- Process Areas organize resources into logical categories
- Multiple processes can be performed on a single resource
- Parameters ensure consistent, repeatable results
Processes
Overview
A process is a documented recipe or procedure that defines exactly how to perform an operation on a resource. It includes specific parameters, settings, and steps required for consistent results.
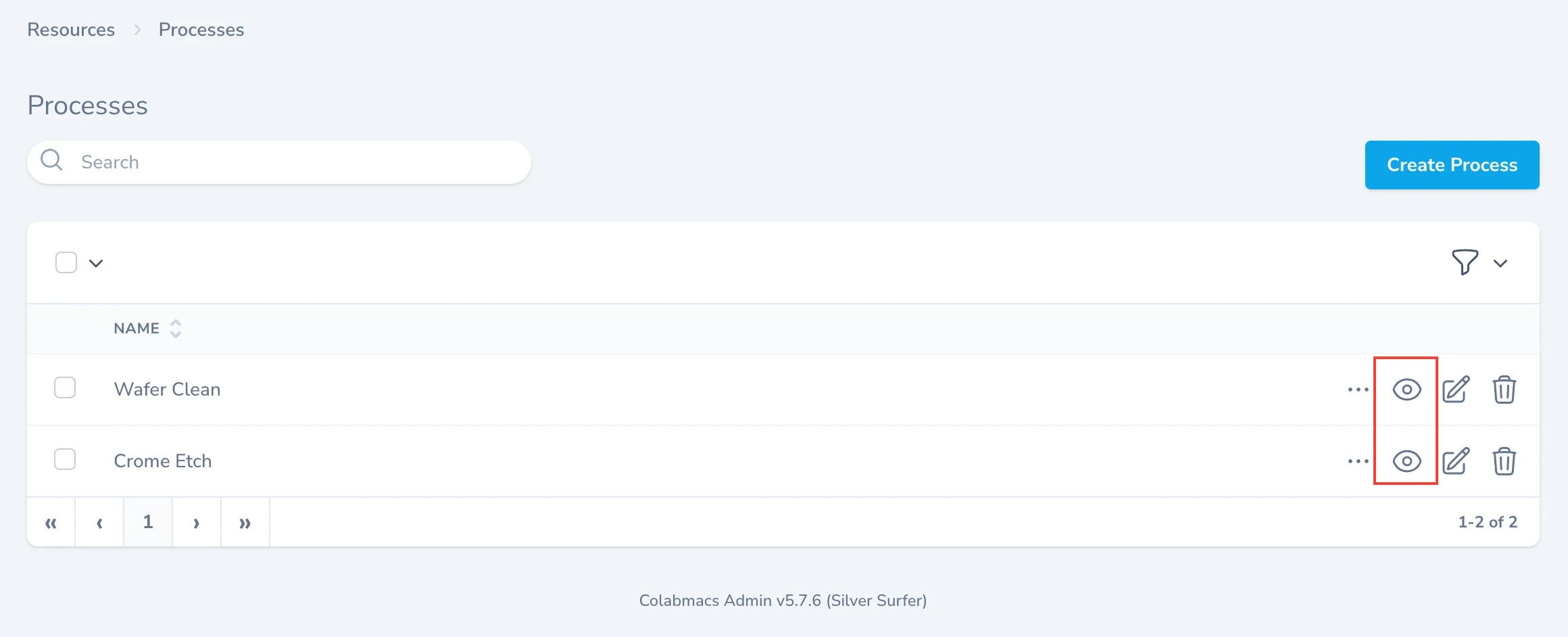
Viewing Processes
Navigate to Resources → Processes to view all defined processes.
Empty processes page
Page Elements:
- Search Bar - Filter processes by name
- Filter Icon - Advanced filtering options
- Create Process Button - Add new process recipes
Creating a Process
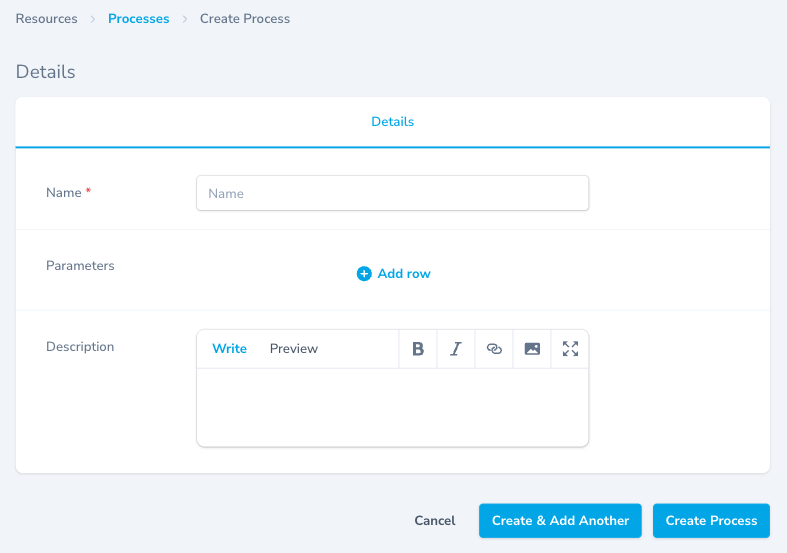
Step 1: Fill in Process Details
Name (Required)
- Enter a descriptive name for the process/recipe
- Be specific about what the process accomplishes
- Examples:
Aluminum Anodizing - Type IIPLA 3D Print - Standard QualityPCB Etching - CopperFabric Dyeing - Cotton BlueCNC Milling - Aluminum Finishing
Parameters Click Add row to define each process parameter with exact values:
Common Parameter Types:
Time-Based:
time: 30 mincure time: 2 hoursdwell time: 45 sec
Temperature:
temp: 365 ºCpreheat temp: 180 ºCcool down temp: 25 ºC
Power/Energy:
power: 150 Wvoltage: 220 Vcurrent: 5 Alaser power: 40%
Material Quantities:
Liquid 1: 50 mLLiquid 2: 15 mLpowder weight: 25 gfilament: PLA 1.75mm
Speed/Rate:
feed rate: 100 mm/minspindle speed: 3000 RPMflow rate: 5 L/min
Pressure:
chamber pressure: 5 PSIvacuum: 0.1 Torr
Concentration:
HCl concentration: 15%solution ratio: 3:1
Distance/Dimension:
layer height: 0.2 mmcut depth: 2 mminfill: 20%
Example Process Parameters:
3D Printing - PLA Standard:
temp: 210 ºC
bed temp: 60 ºC
print speed: 60 mm/s
layer height: 0.2 mm
infill: 20%
time: 3 hoursChemical Etching - PCB:
Ferric Chloride: 500 mL
temp: 45 ºC
agitation: continuous
time: 15 min
rinse water: 2 LCNC Milling - Aluminum:
spindle speed: 3000 RPM
feed rate: 100 mm/min
cut depth: 2 mm
coolant flow: 5 L/min
tool: 6mm end millDescription
- Provide step-by-step instructions for the process
- Include safety warnings and PPE requirements
- Note any prerequisites or preparation steps
- Add troubleshooting tips
- Supports rich text formatting (Bold, Italic, Links, Images)
Description Example:
## Safety Requirements
- Wear safety glasses and gloves
- Ensure proper ventilation
- Keep fire extinguisher nearby
## Preparation
1. Clean resource surface
2. Prepare materials according to parameters
3. Verify all settings before starting
## Procedure
1. Preheat to specified temperature
2. Load material into chamber
3. Set parameters as listed
4. Monitor first 5 minutes closely
5. Allow full cool-down before removing
## Post-Processing
- Inspect for quality
- Clean resource after use
- Log any issuesStep 2: Save
Choose:
- Create Process - Save and return to list
- Create & Add Another - Save and create another process
- Cancel - Discard changes
Managing Processes
Edit Process:
- Click on process name or pencil icon
- Modify parameters or description
- Click Update Process
Delete Process:
- Select process checkbox
- Click trash icon
- Confirm deletion
View Details:
- Click eye icon to view complete process recipe
- See all parameters and instructions
Version Control Tip: When updating a process, consider creating a new version (e.g., "Aluminum Anodizing v2") rather than modifying the original if parameters change significantly.
Process Areas
Overview
Process Areas are simple categories that organize resources by type or department. They help users quickly find resources related to specific types of work.
Viewing Process Areas
Navigate to Resources → Process Areas to view all areas.
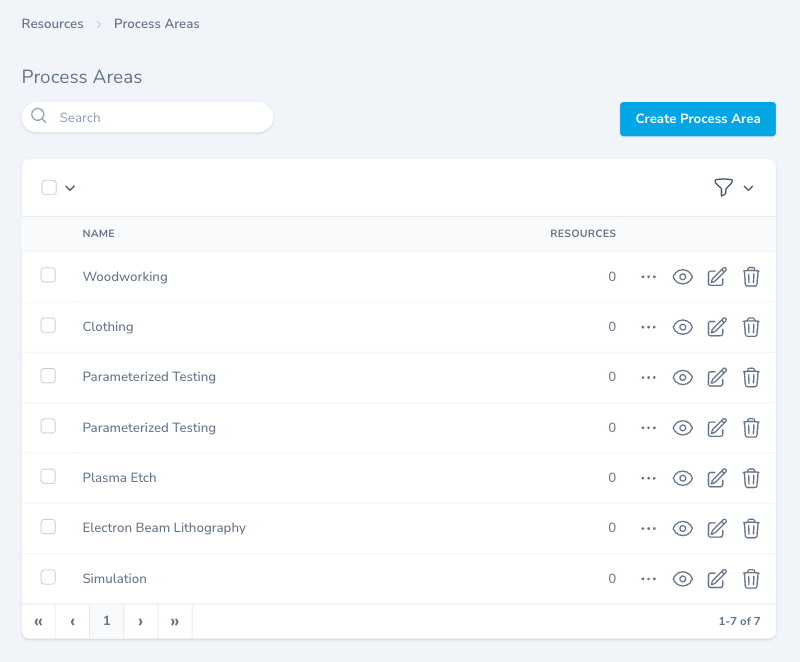 Process Areas listing page
Process Areas listing page
Table Columns:
- NAME - Process area category
- RESOURCES - Number of resources in this area
Common Process Areas:
| Area | Typical Resources | Example Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Soldering stations, oscilloscopes, power supplies | PCB assembly, circuit testing |
| Textiles | Sewing machines, embroidery, fabric cutters | Garment construction, dyeing |
| Woodworking | Table saws, lathes, sanders, routers | Furniture making, finishing |
| Packaging | Heat sealers, labelers, shrink wrap | Product packaging, sealing |
| Wet Processing | Etching tanks, chemical baths, cleaning | Chemical etching, cleaning, coating |
| 3D Printing | FDM printers, resin printers, filament dryers | PLA printing, resin printing |
| Machining | Mills, lathes, grinders | Metal cutting, drilling, turning |
| Laser Cutting | CO2 lasers, fiber lasers | Acrylic cutting, metal engraving |
| Clean Room | Lithography, deposition, etching | Semiconductor processing |
| Ceramics | Kilns, pottery wheels, glaze stations | Firing, glazing |
Actions:
- 👁 View area details
- ✏ Edit area
- 🗑 Delete area
Creating a Process Area
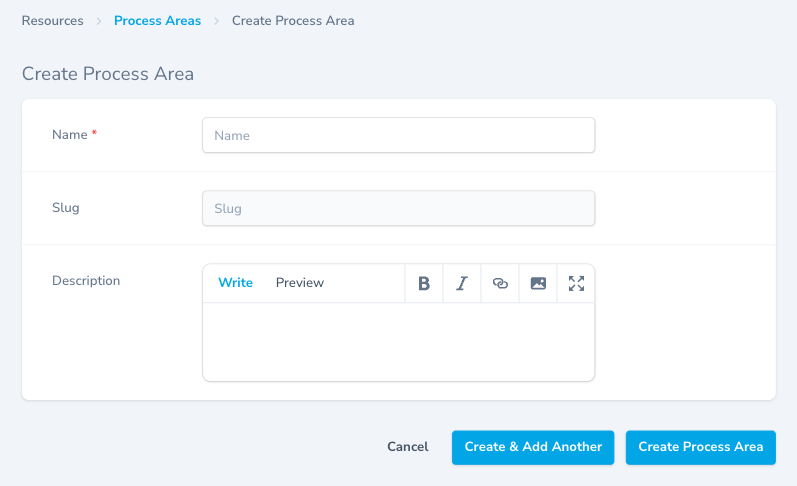
Step 1: Fill in Area Details
Name (Required)
- Enter a category name that groups similar resources
- Use department names, material types, or work categories
- Keep names simple and recognizable
Good Examples:
ElectronicsWoodworkingTextilesWet Processing3D PrintingMetalworkingPackagingCeramicsPlasticsClean Room
Slug
- URL-friendly identifier (auto-generated from name)
- Used in web addresses
- Example:
electronics,wet-processing,3d-printing
Description
- Brief overview of what types of resources belong in this area
- List example resources
- Note any special access requirements
- Supports rich text formatting
Description Example:
The Electronics area includes all resources for electronic circuit design,
assembly, and testing. This includes soldering stations, oscilloscopes,
power supplies, and testing equipment.
Access requires basic electronics safety training.Step 2: Save
Choose:
- Create Process Area - Save and return to list
- Create & Add Another - Save and create another area
- Cancel - Discard changes
Managing Process Areas
Edit Process Area:
- Click on area name or pencil icon
- Modify name, slug, or description
- Click Update Process Area
Delete Process Area:
- Select area checkbox
- Click trash icon
- Confirm deletion
⚠️ Warning: Deleting a process area removes the category assignment from all associated resources.
View Associated Resources:
- Click eye icon to see all resources in this area
- Check resource count in RESOURCES column
How Processes and Resources Work Together
Process-Resource Relationship
A resource can have multiple processes defined for it:
Example: CNC Mill Resource
Resource: CNC Mill XYZ-3000
Associated Processes:
├── Aluminum Milling - Rough Cut
│ └── spindle speed: 2500 RPM, feed rate: 150 mm/min
├── Aluminum Milling - Finish Cut
│ └── spindle speed: 3500 RPM, feed rate: 80 mm/min
├── Steel Milling - Standard
│ └── spindle speed: 2000 RPM, feed rate: 100 mm/min
└── Plastic Milling - Acrylic
└── spindle speed: 4000 RPM, feed rate: 200 mm/minEach process provides exact parameters for different operations on the same resource.
Process-Specific Training
Training may be required for specific processes. Users must complete process training before they can use that process on a resource.
Training Requirements:
Resource: CNC Mill XYZ-3000
├── Standard Training: "CNC Mill Basic Operation" (required for all processes)
└── Process-Specific Training:
├── "Aluminum Milling Certification" → Required for aluminum processes
├── "Steel Milling Certification" → Required for steel processes
└── "Advanced Finishing" → Required for finish cut processesAccess Control:
- User must complete standard resource training first
- Additional training required for specific processes
- User can only select processes they are trained for
- Ensures safety and quality for specialized operations
Example:
User: John Smith
Completed Training:
✓ CNC Mill Basic Operation
✓ Aluminum Milling Certification
Available Processes:
✓ Aluminum Milling - Rough Cut
✓ Aluminum Milling - Finish Cut
✗ Steel Milling - Standard (requires Steel Milling Certification)
✗ Plastic Milling - Acrylic (requires Plastics Training)Workflow Example
Scenario: User wants to mill aluminum part
- Select Resource: CNC Mill XYZ-3000 (in Machining area)
- Verify Training: User has completed:
- CNC Mill Basic Operation ✓
- Aluminum Milling Certification ✓
- Choose Process: "Aluminum Milling - Finish Cut" (now available)
- View Parameters:
- spindle speed: 3500 RPM
- feed rate: 80 mm/min
- cut depth: 1 mm
- coolant: flood cooling
- tool: 6mm carbide end mill
- Follow Instructions: Step-by-step procedure from process description
- Complete Operation: Using exact parameters for consistent results
Example: Complete Process Setup
Facility: University Makerspace
Process Areas:
- Electronics
- 3D Printing
- Laser Cutting
- Woodworking
- Textiles
Example: Laser Cutting Area
Resources:
- Laser Cutter - Model A (100W CO2)
- Laser Cutter - Model B (60W CO2)
Processes for Model A:
1. Acrylic 3mm - Cut
power: 80%
speed: 10 mm/s
passes: 1
air assist: on
focus height: 0 mm2. Acrylic 3mm - Engrave
power: 30%
speed: 300 mm/s
passes: 1
air assist: off
focus height: 0 mm3. Plywood 6mm - Cut
power: 100%
speed: 5 mm/s
passes: 2
air assist: on
focus height: 0 mmResult: Users select the appropriate process based on their material and operation, ensuring consistent results and reducing errors.
