Locations
11/16/25About 2 min
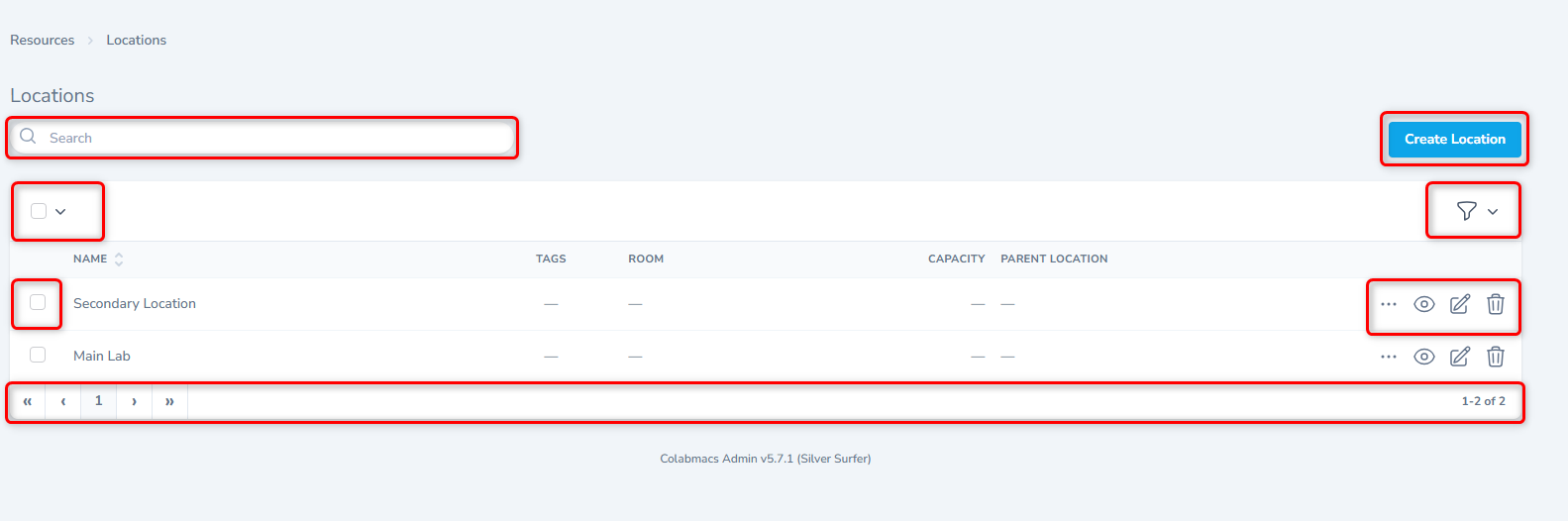
Locations
About Locations
The Locations feature allows you to precisely manage and define all physical spaces within your facility. You can add, view, update, and delete location details, ensuring accurate mapping of your resources.
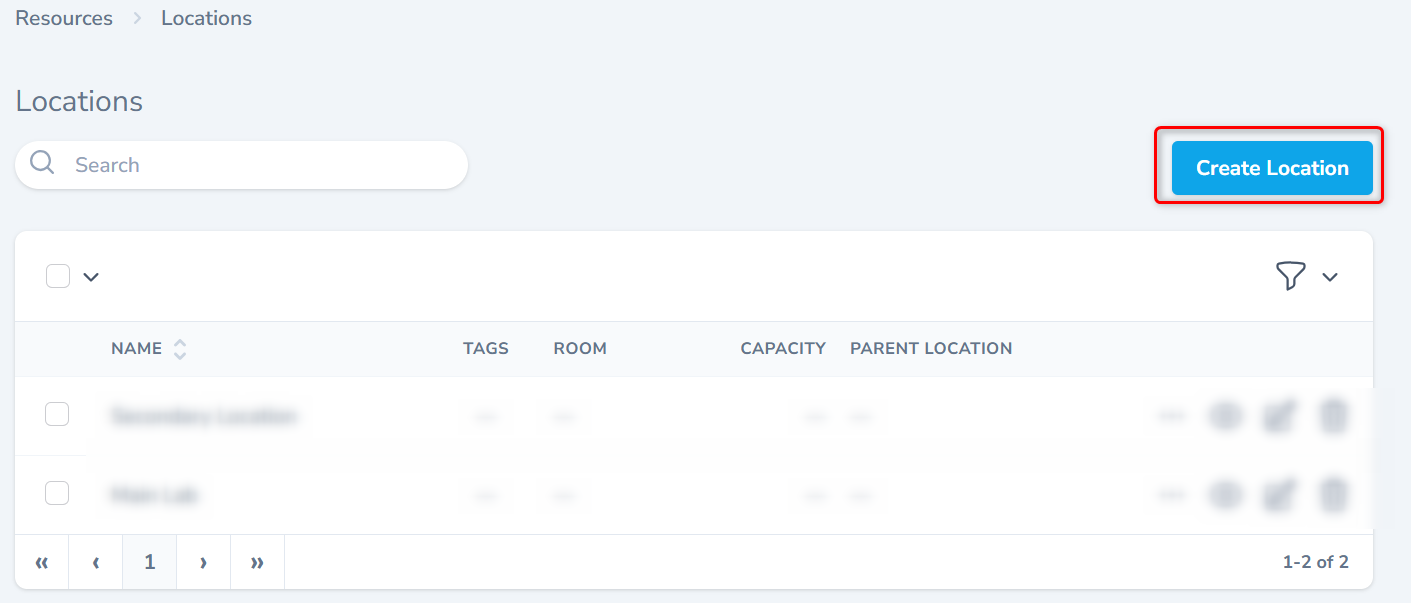
Create New Location
From the listing screen, click the Create Location button.
The system will display the form shown below. Fill in the appropriate details to create a new location.
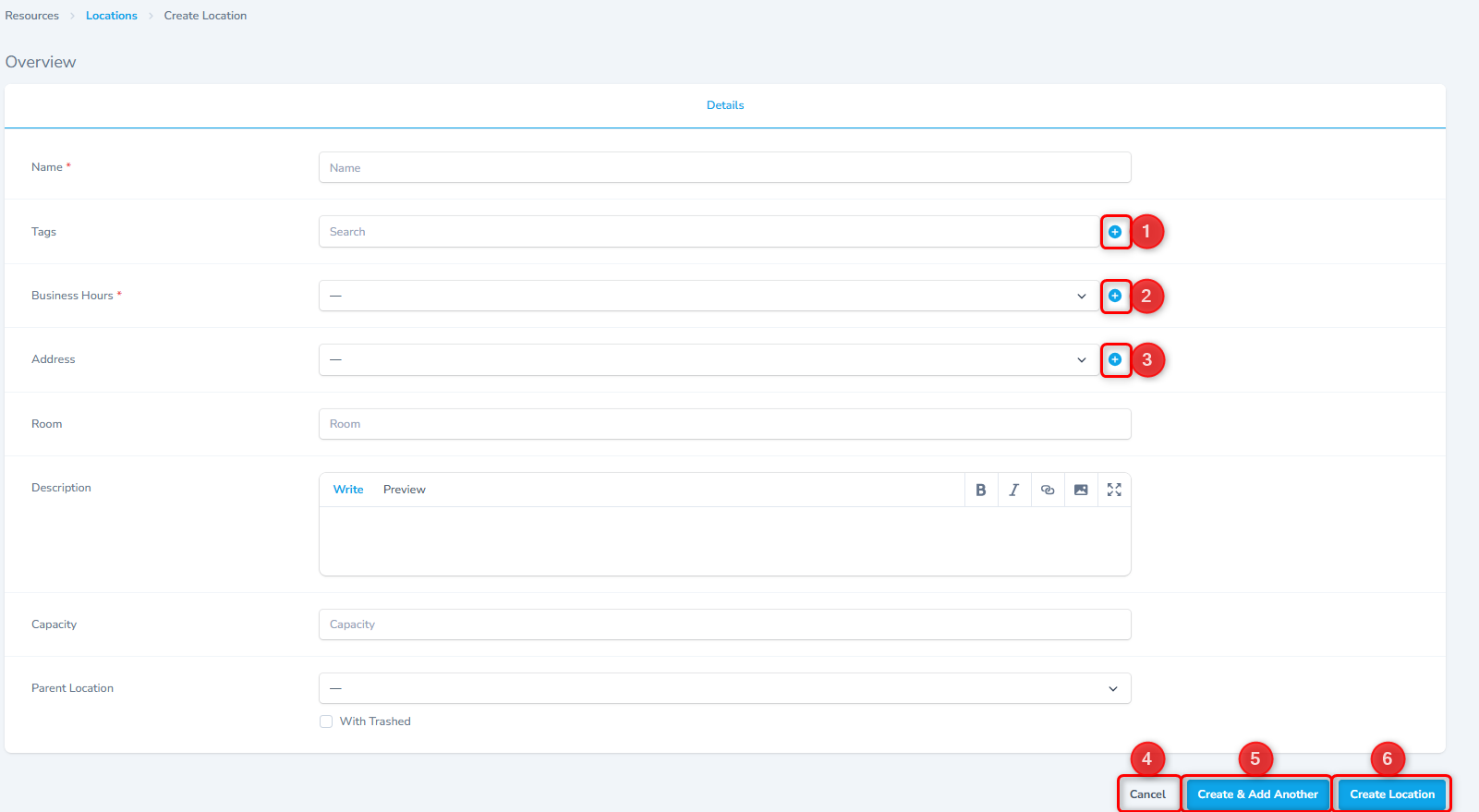
- Enter the name of the location.
Associate/Create New Tag
- Enter the phrase to search an existing tag and associate the tag with this location.
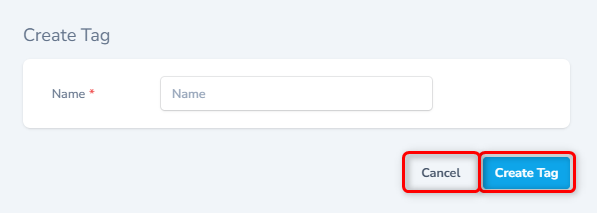
- To create a new tag and associate with this location, click the + button against the Tags field (Shown as #1 in the screen above)
- Enter the name of the Tag and click Create Tag button to create a new tag and associate it with this current location.
- To close this dialog without any changes, click Cancel.
- For details, please refer to the screen below.
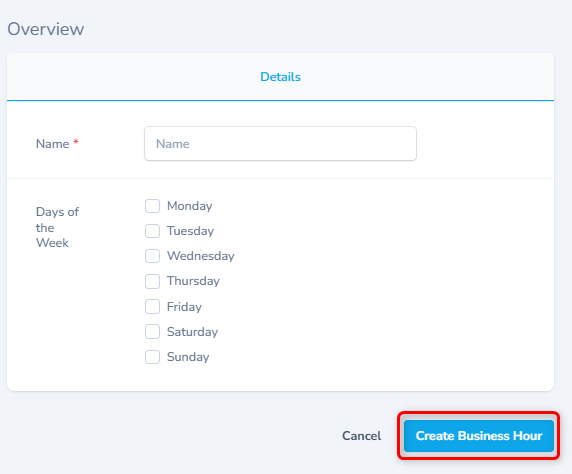
Associate/Create New Business Hours
- Select the Business Hours from the drop down.
- To create a new Business Hour record and associate with this location, click the + button against the Business Hour field (Shown as #2 in the screen above)
- Enter the name of the Business Hour, select the work days and click the Create Business Hour button to create a new record.
- To close this dialog without any changes, click Cancel.
- For details, please refer to the screen below.
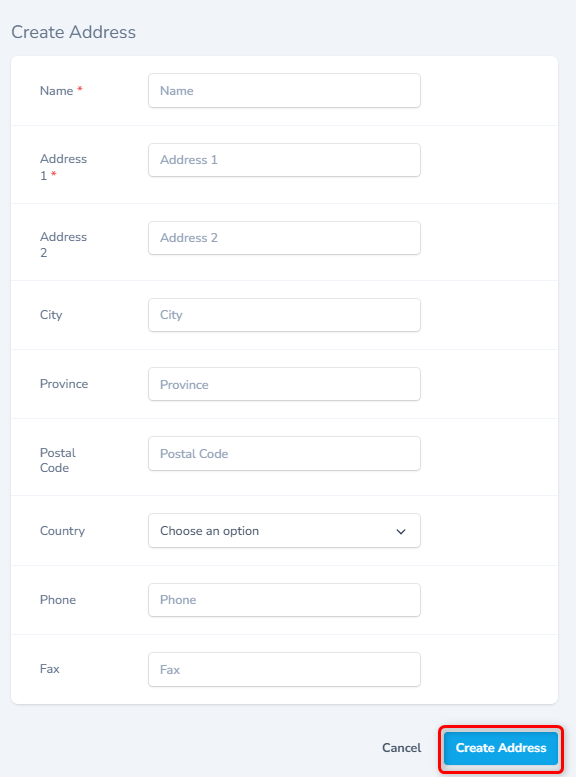
Associate/Create New Address
- Select the Address from the drop down.
- To create a new Address record and associate with this location, click the + button against the Address field (Shown as #3 in the screen above)
- Enter appropriate details and click the Create Address button to create a new record.
- To close this dialog without any changes, click Cancel.
- For details, please refer to the screen below.
Save Record
- Fill all the remaining fields, i.e., Room, Description, Capacity.
- If the location is a child location, then associate the parent location by selecting appropriate value in the Parent Location field.
- To save the record, click the Create Location button.
- To save this record and add another record, click the Create & Add Another button.
- To close without saving, click the Cancel button.
Tip
When adding multiple location, use the Create & Add Another function to add records more efficiently.
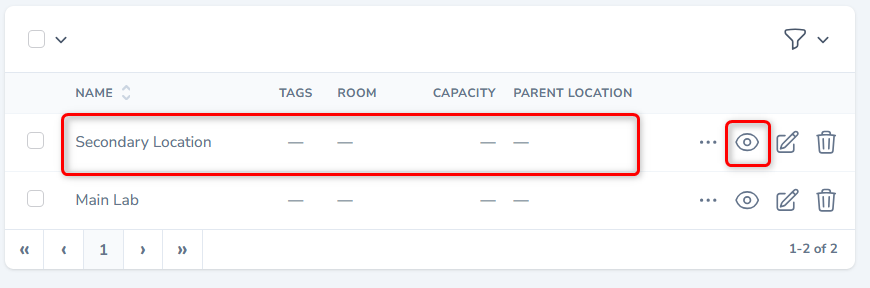
View Record
- From the listing screen, click the View button or click the record. The system will display a detailed form as shown.

Overview Section
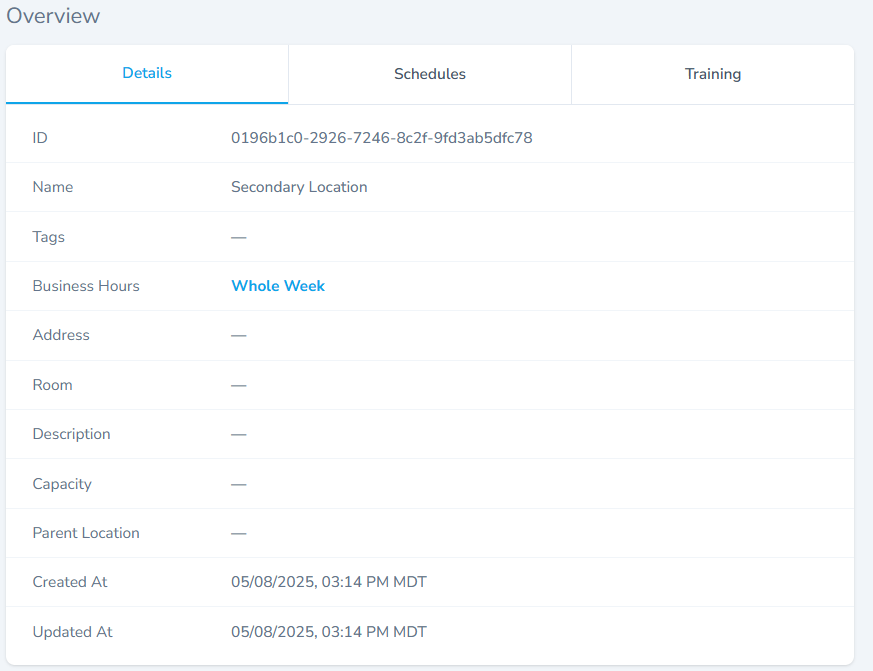
- The overview section has three tabs, Details tab, Schedules tab, Training tab.
- The Details tab shows core location information.
- The Schedules tab allows to attach a schedule with the location.
- The Training tab allows to configure / associate trainings with this specific location.
Info
Refer to the Schedule Module, Trainings and Training Management for more details.
Info
Refer to the for more details.
Resources Section
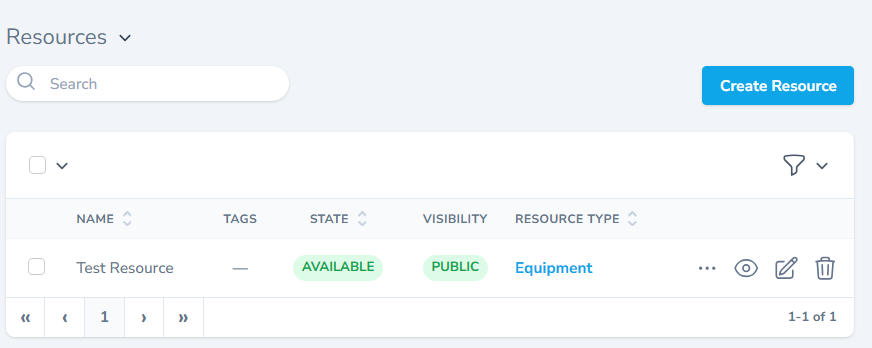
- The resources section lists all the available resources.
- The section also allows you to create a new records alongside viewing, editing and deleting options.
Info
Refer to the Resources Module for more details.
Sublocation Section
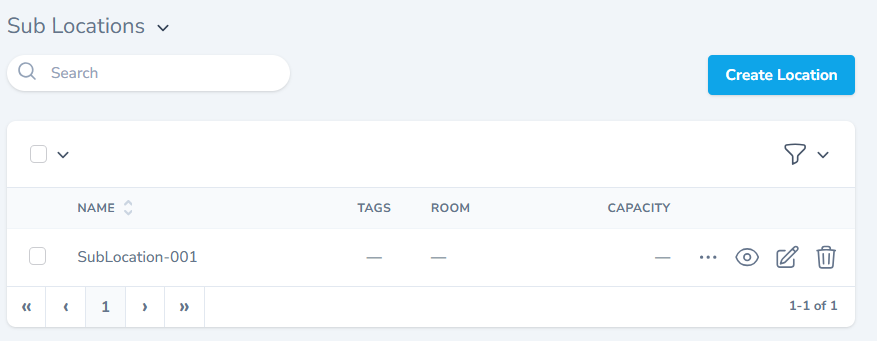
- The Sublocation section allows users to create a location under a location.
- This is very helpful in creating a Hierarchical Location Structure.
- The section also allows you to create a new records alongside viewing, editing and deleting options.
Access Rules Section
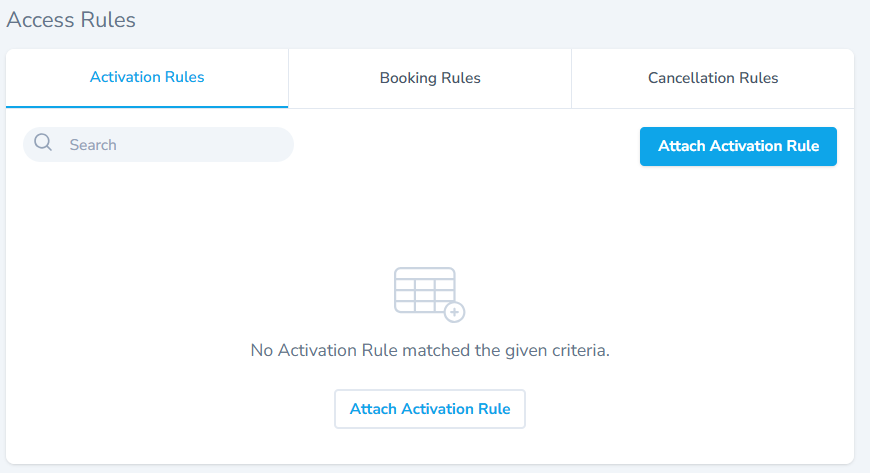
- The Access Rules section allows users to create and attach access rules to a location.
- The overview section has three tabs, Activation Rules tab, Booking Rules tab, Cancellation tab.
- The Activation Rules tab shows all the activation rules.
- The Booking Rules tab displays all the booking rules.
- The Cancellation Rules tab shows all the cancellation rules.
Info
Refer to the Access Rules Module for more details.
Downtime Section
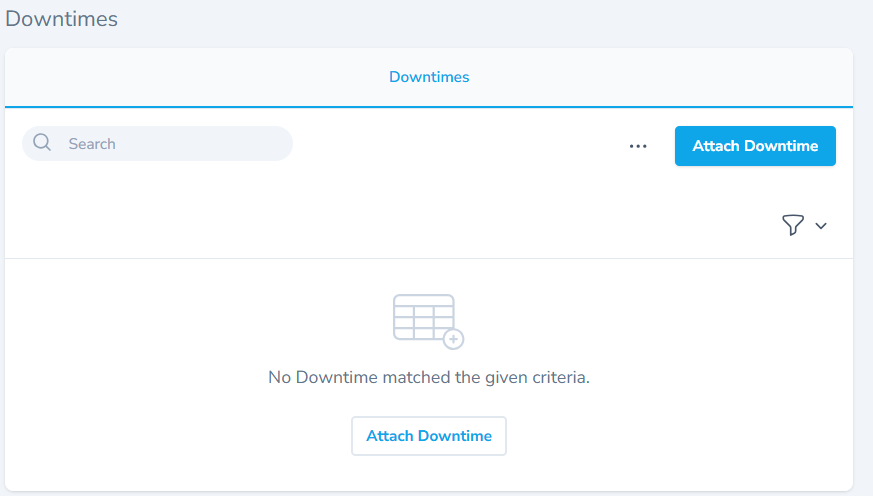
- The downtime section allows users to associate downtime states to a location.
- The section also allows you to search and filter records.
Info
Refer to the Schedules Module for more details.
